 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
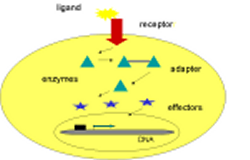
In general signaling
many hormones, cytokines, growth factors or neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the cell-membrane. The signal is transmitted through the receptor to other signaling mediators in the cell, like
- enzymes
- adapter proteins
- effector proteins
The ligand-activated state is gene-regulation through specific effector proteins which activate transcription factors. |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Figure 1: General signaling |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interleukin-1 |
|
|
|
|
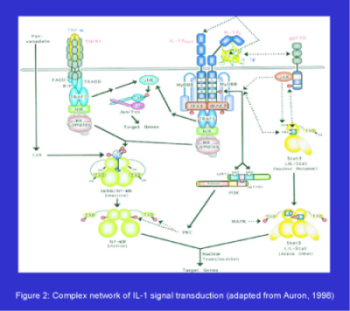
IL-1 (interleukin-1) is a pivotal pro-inflammatory cytokine centrally involved in local and systemic responses in the immune system leading to typical effects of inflammation. Dysregulated, prolonged
synthesis and release of IL-1 in chronic inflammatory situations contributes to many diseases, e.g. rheumatoid arthritis. Because of its importance in these diseases more research has to be done on IL-1 signaling. Figure 2
shows a likely and possible network of pathways associated with IL-1 signal transduction and its interconnection with the related TNF (tumor necrosis factor) signal transduction. TNF also represents an pro-inflammatory cytokine that leads to many inflammatory diseases as known for IL-1.
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IL-1 pathway |
|
|
|
|
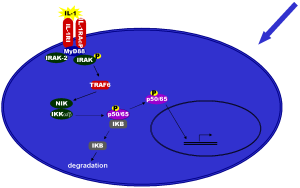
In IL-1 signaling the signal-mediating IL-1 receptor Type I (IL1-RI) forms a heterodimer with a second molecule (Figure 3), the IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP). Binding of IL-1 to this receptor complex leads to
activation of the transcription factor NF B through different signaling molecules. B through different signaling molecules.
DNA-binding motifs for NF B are found in the promotors and enhancers of many genes that are known to be activated upon inflammation. B are found in the promotors and enhancers of many genes that are known to be activated upon inflammation. |
|
|
TRANSPATH objectives and content |
|
|
|
We are aiming to construct a comprising database for two reasons: primarily there is a demand for structuring the
growing amount of signal transduction data. Secondly in order to predict cellular responses simulation models can be established on the comprehensive database. To give a clue about how data is implemented in TRANSPATH the IL-1
signaling as an example is given.
The main entries of TRANSPATH are signal molecules and reactions/ interactions that build up a coherent, detailed system. Further information can be obtained by other linked databases such as
TRANSFAC, Cytomer, PathoDB, S/MARt DB, Swissprot or EMBL.
Visualization is a useful tool to summarize the information about the complex signaling network. Therefore schematic figures are integrated into TRANSPATH. Figure 3 represents the IL-1 signal transduction. |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|






