|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
|
High Quality Annotation |
|
|
|
|
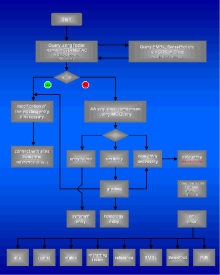
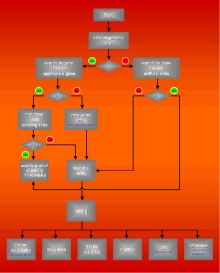
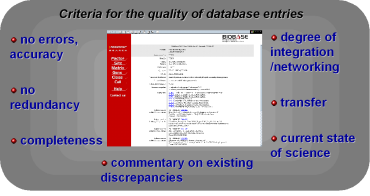
It is obvious that the quality of the data annotation process can be assessed by its products. But what are high quality
data entries? Some criteria can be set up, which are closely linked to the annotation process (Fig.1). Of course main focus is on accuracy. No error should occur, whatever it is: syntax error, systematic error,
textual error or typing error. Zero tolerance for errors is an important principle of modern quality management.
There should be no redundancy in the database and the complete extraction of given, relevant data is a desirable
aim. Other criteria are the degree of integration and the analysis and densification of data, which is a transfer to a higher information level (e.g. the generation of TRANSFAC matrizes). |
|
|
Also, as quality is the fulfillment of customer requirements (ISO 8402), the implemented data has to be fit for usage. |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Fig. 1
: Criteria for the quality of database entries |
|
|
|
|
|
|
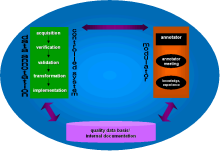
Fig. 2
shows a simple model for the regulation of quality analogous to control theory. The annotator as a modulator regulates the process of data annotation (the controlled system) and can fall back on the pool of quality data. The regular annotator meeting serves as a communication tool, important for the transfer of knowledge, definition of format, syntax and other conventions. The aim of the internal documentation system is to collect all this information, being itself part of a company-wide information system.
|
|
|
|
Internal Documentation for TRANSFAC |
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 2: Model for quality
regulation in data annotation |
|
|
The internal documentation for TRANSFAC exists as a couple of browsable, HTML-formatted files, which are accessible over a portal site. It is integrated into the BIOBASE
annotation homepage. As the documentation contains proprietary information of BIOBASE, it is for internal use only. |
|
|
|