|
 |
 |
 |
|
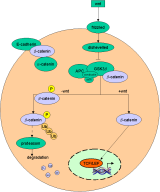
A simple model of the wnt-pathway |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
Fig. 1 |
|
|
|
b-catenin besides the wnt pathway |
|
|
b-catenin is also involved in the formation of adherens
junctions of mammalian epithelia where it links a-catenin to E-cadherin. E-Cadherin
and APC compete for interaction with b-catenin. |
|
 |
 |
|
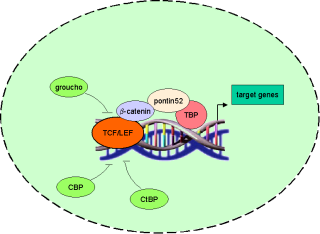
b-catenin in the wnt pathway |
|
|
Binding of wnts (secreted glycoproteins) to frizzled receptors activate dish-evelled which blocks the function of a complex assembled
over certain scaffold proteins (axin/ conduction).
These complexes can promote the phosphorylation of b-catenin by GSG-3b (glycogen synthase kinase
3b) in the absence of wnts (-wnt). Thus phosphorylated b-catenin becomes ubiquiti-nated and degraded by proteasomes.
In the presence of wnt signals (+wnt) the
cytosolic amount of b-catenin increases and thus translocates to the nucleus where it
associates with transcription factors of the TCF/ LEF family. Due to its transactivating ability the b-catenin-transcription-factor-co mplex binds to DNA and activates wnt target genes. |
|
 |
 |
|
TCF/ LEF transcription factors and target genes |
 |
 |
|
The founding members of the TCF/ LEF family of transcription factors were independently cloned in 1991: human T-cell factor 1
(TCF-1), mouse lymphoid enhancer factor (LEF-1) and human LEF-1 showed high binding affinity to (A/T)(A/T)CAA(A/T)GG-sequences.
According to the fact that these factors comprise a common DNA binding motif of about
80 amino acid length (HMG-box) which binds to DNA´s minor groove these factors where grouped into the HMG box family (TRANSFAC class 4.7).
Until now 70 binding sites for TCF/ LEF transcription factors have been recorded in TRANSFAC (see table 1). |
|